KEYPOWER Team’s Cummins Study Tour
Aug 28, 2025
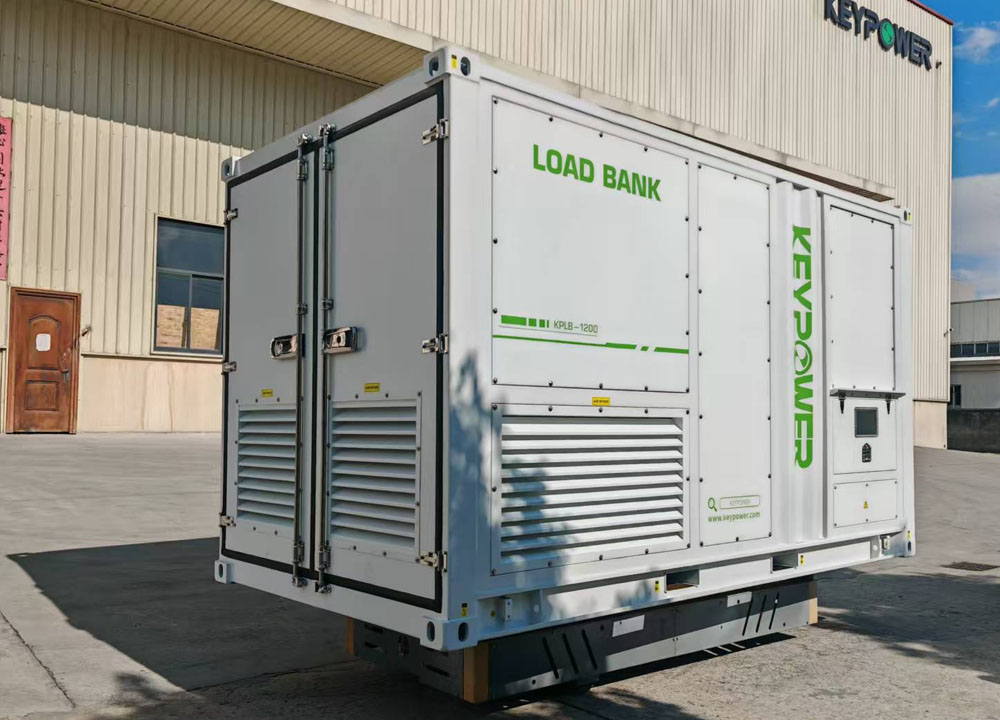
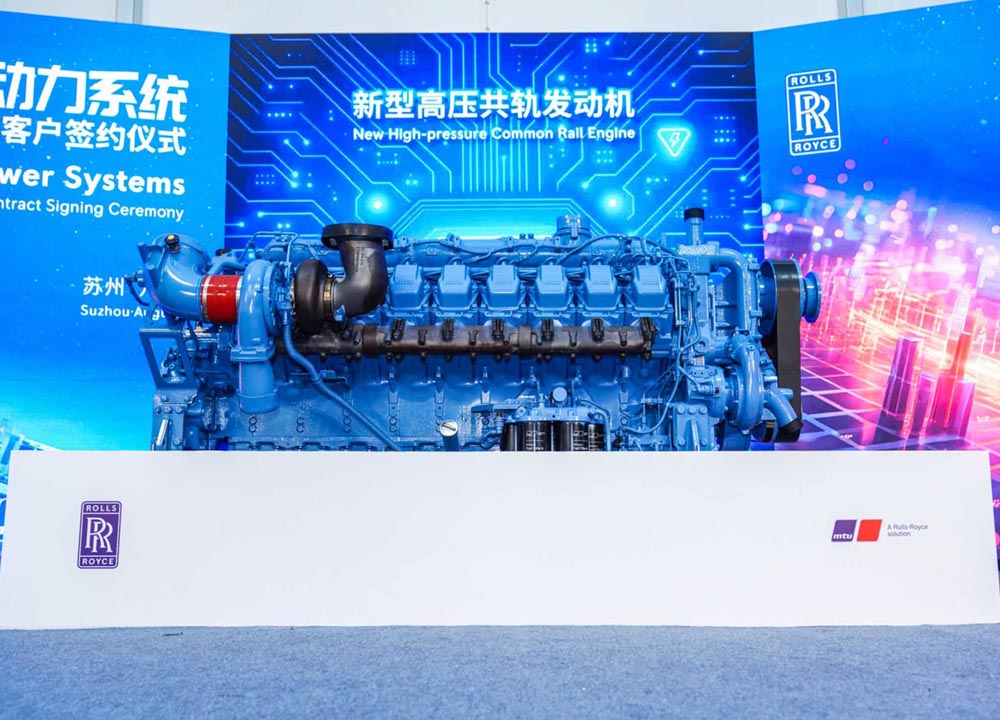
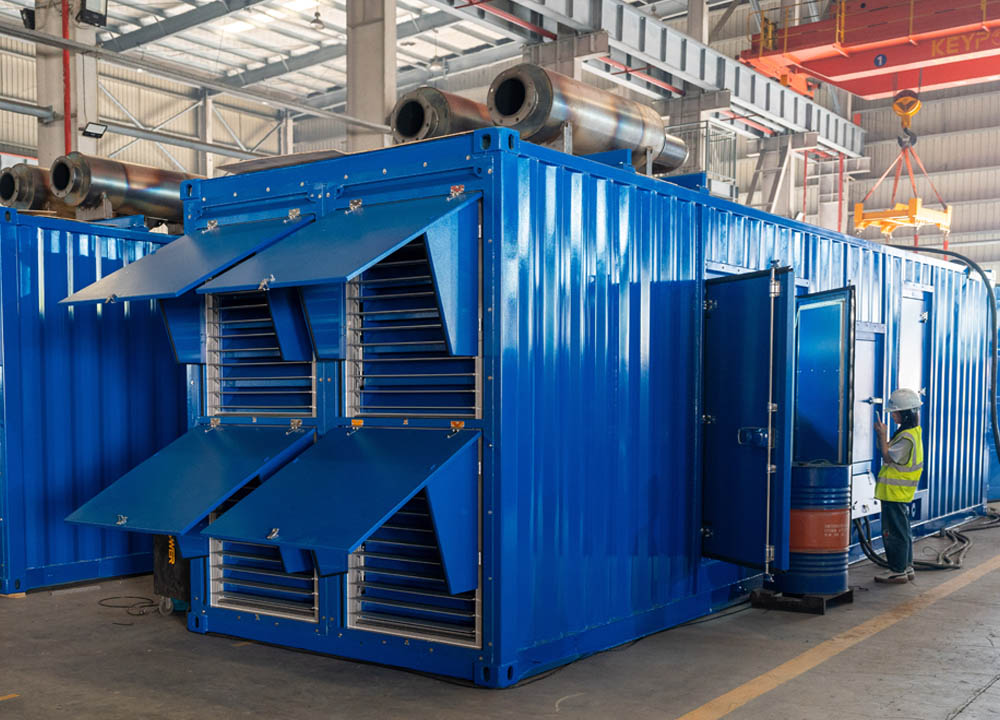
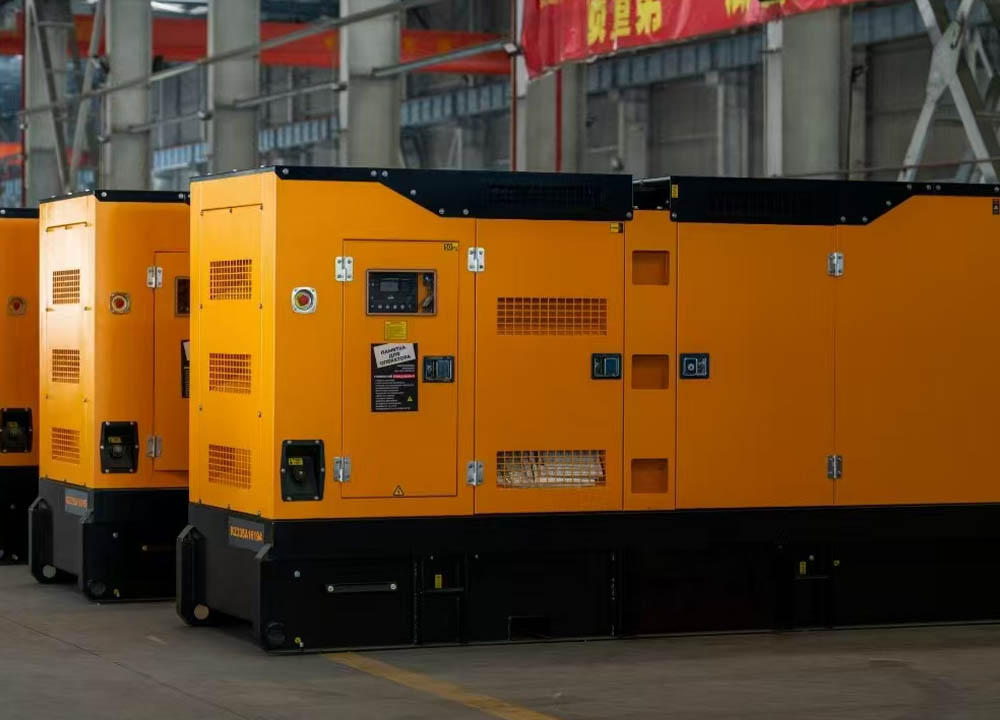
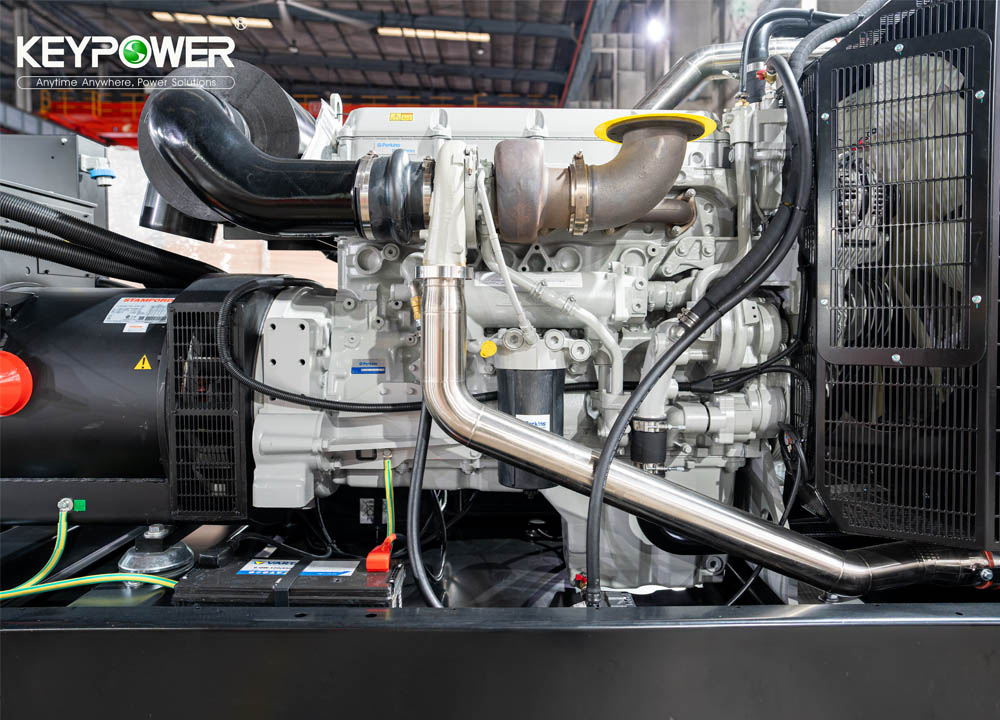
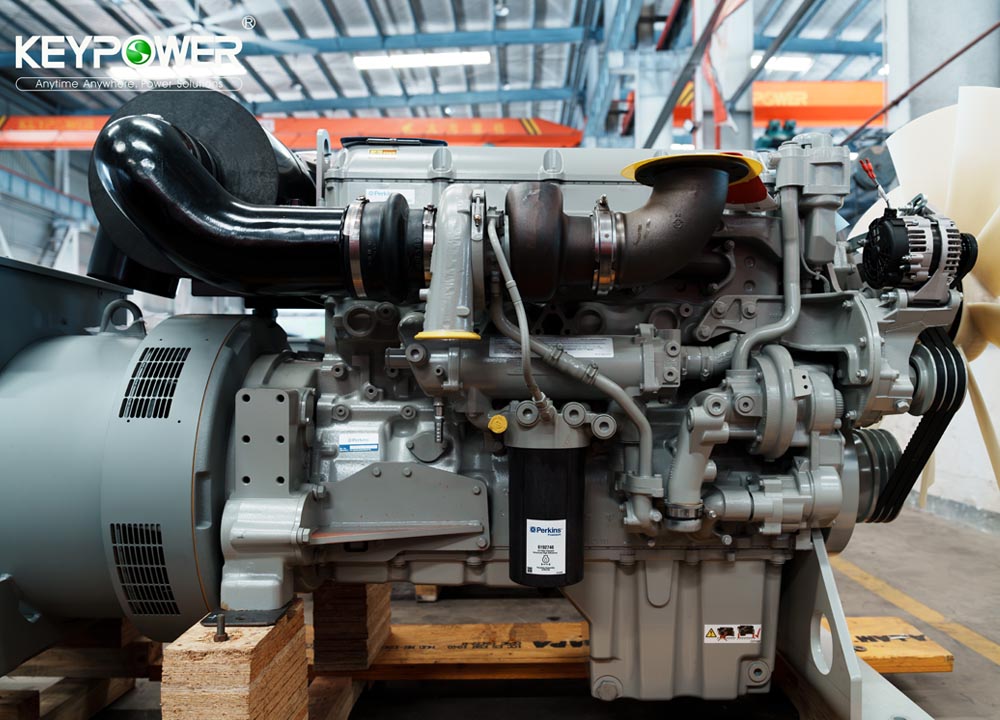
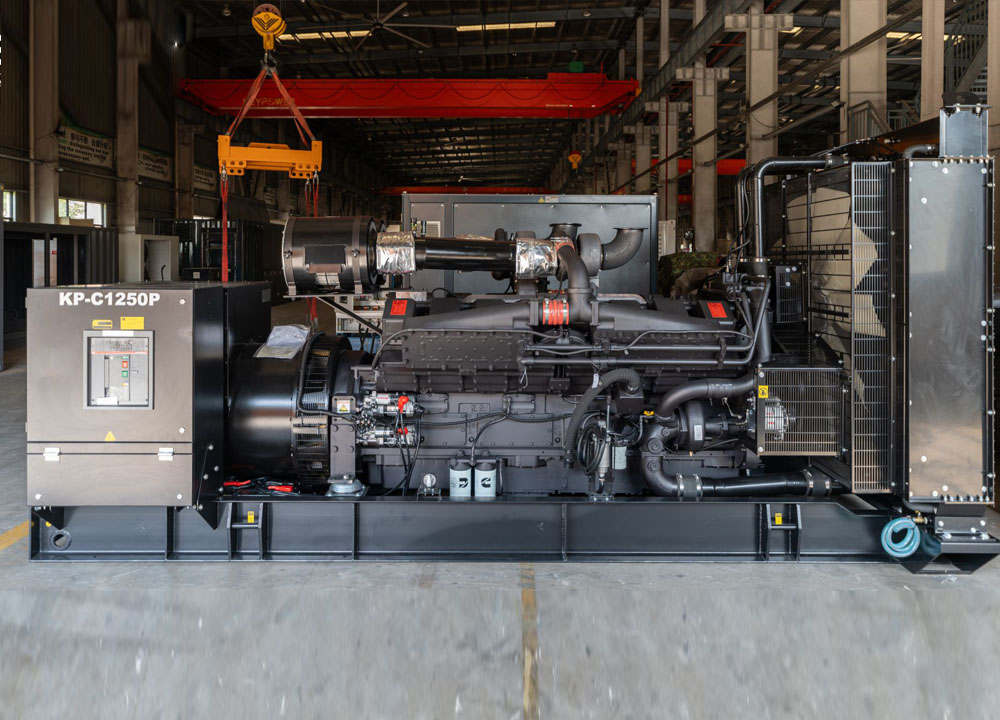
In late August, the KEYPOWER team embarked on a systematic and enriching study tour to Cummins, visiting both Dongfeng Cummins (DCEC) and Chongqing Cummins (CCEC). From the production lines to R&D laboratories, from product training to after-sales services, the team gained a comprehensive understanding of Cummins' exceptional capabilities and innovative spirit as a global leader in power solutions. Visit to Dongfeng Cummins: Lean Manufacturing and Professional EmpowermentOn the morning of August 21, the production team leader at Dongfeng Cummins guided the KEYPOWER team through the DCEC factory production line. The highly automated management systems, efficient production layout, and human-centric work environment significantly enhanced operational efficiency, reflecting Cummins' outstanding manufacturing philosophy. In the afternoon, the DCEC sales manager, along with pre-sales and after-sales teams, conducted systematic training on product selection and after-sales services for the KEYPOWER team, further strengthening our comprehensive capabilities in customer support. On the morning of August 22, the team visited two gas generator partner factories to gain practical insights into the core components and operational principles of gas engines. Subsequently, the sales director and their team led a tour of the CPT factory, where the sight of thousands of engines ready for shipment showcased Cummins' strong order fulfillment and market responsiveness. In the afternoon, the team visited Langhong Radiator Factory, DCEC's designated radiator supplier, observing the complete production process from raw materials to finished products. The team was particularly impressed by the customized C5-protected radiators and the world's largest radiator, both exemplifying remarkable craftsmanship and technology. Chongqing Cummins Visit: Technology Leadership and Collaboration DeepeningOn August 25, the general manager of the sales department and the technical market application team provided KEYPOWER with specialized training on product selection and power technology, helping us better understand product matching and differentiated needs. The company's general manager warmly received the team and joined them for a group photo. In the afternoon, the team toured the CCEC factory production line and laboratory, with a special focus on China's largest power laboratory. The advanced testing equipment and stringent validation standards demonstrated Cummins' leading position in R&D and quality. On August 26, the after-sales service team lead systematically explained engine maintenance knowledge and international after-sales service processes, enhancing our ability to support overseas markets. The following day, the gas department manager conducted further training on gas power technology, covering structural principles, application scenarios, and maintenance essentials. This provided critical support for KEYPOWER's business expansion in the gas generator set sect...
Read More
 English
English English
English français
français Deutsch
Deutsch русский
русский español
español português
português Nederlands
Nederlands العربية
العربية Polski
Polski 中文
中文














 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported